The Technology Behind Zephyr Air Purifiers
Sick Building Syndrome
ZEPHYR AIR PURIFIERS USE 7 DIFFERENT STAGES AND TECHNOLOGIES TO FILTER THE AIR YOU BREATHE IN YOUR HOME OR OFFICE. HERE IS AN IN DEPTH LOOK INTO THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY BEHIND EACH STAGE.
HEPA Filters are one of the most trusted filtration technologies in the world, used by hospitals, high tech clean rooms, and scientific laboratories. HEPA is an acronym for “High Efficiency Particulate Air” and/or “High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance”. It is important to understand that not all HEPA Filters are made the same and thus provide differing results. Cheaper made HEPA Filters or “HEPA – type, HEPA – style or HEPA – like Filters” are made from nonwoven glass fibers (fiberglass) and thus have a lower filtration efficiency.
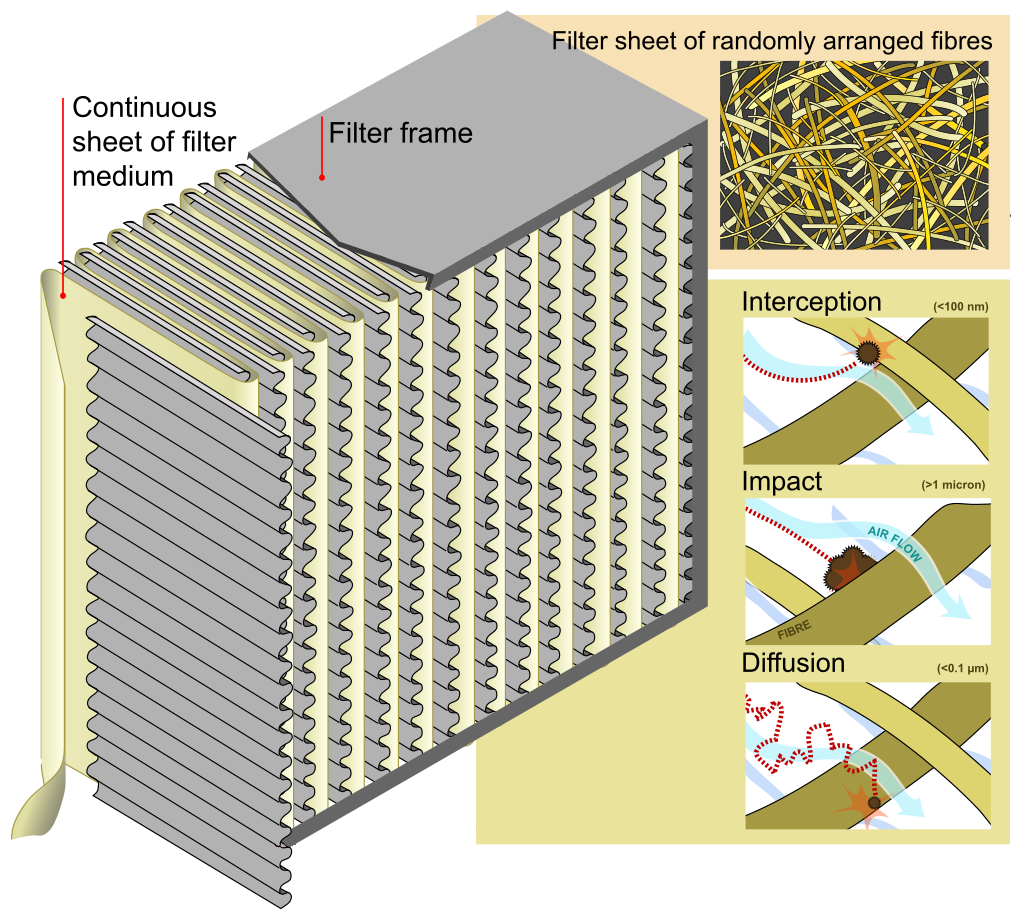
Our HEPA Filters are made from woven randomly arranged PP Fibers (Polypropylene Fibers) for higher filtration efficiency and PP Fibers are chemically inert, meaning they are not chemically reactive; and therefore do not pose any offsetting health risks. Our HEPA filters are designed to target much smaller pollutants and particles down to 0.1 μm in diameter and larger. These particles are trapped (they stick to a fiber) through a combination of the following three mechanisms:
Diffusion: An enhancing mechanism that is a result of the collision with gas molecules by the smallest particles, especially those below 0.1 μm in diameter, which are thereby impeded and delayed in their path through the filter; this behavior is similar to Brownian motion and raises the probability that a particle will be stopped by either interception or impaction; this mechanism becomes dominant at lower air flow.
Interception: Particles following a line of flow in the air stream come within one radius of a fiber and adhere to it.
Impaction: Larger particles are unable to avoid fibers by following the curving contours of the air stream and are forced to embed in one of them directly; this effect increases with diminishing fiber separation and higher air flow velocity.
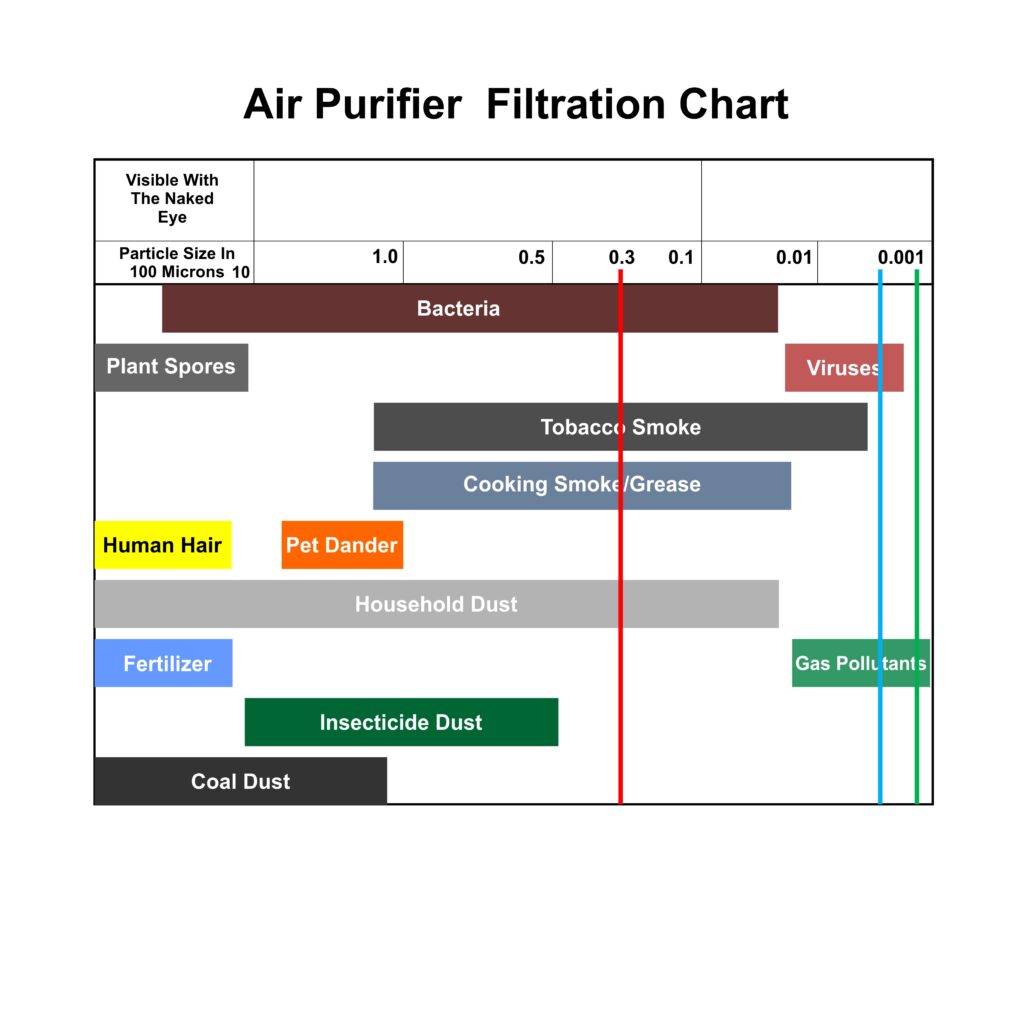
Through these mechanisms, our HEPA Filters are effective at trapping a wide range of particulates including: Dust, pet dander, allergens, pollen, dust mites and their droppings, tobacco smoke.
STAGE 1: PRE-FILTER

It is important to understand that not all carbon filter used in air purifiers are the same. There are two types of filters which are used in air purifiers, one is cheaper and one is more expensive; it is therefore important to understand and know which of these two types of activated carbon filters you are getting when you buy an air purifier.
The first type of filter is a carbon mesh type filter which is widely used by companies due to its very inexpensive manufacturing cost. Unfortunately, the absorption rate of this type of filter is much lower due to a much smaller surface area because there are fewer interconnected series of pores inside the carbon mesh fibers and the air space between fibers allows more pollutants to pass through then the second type of carbon filter.
The second type of carbon filter that can be used in an air purifier is pelletized carbon. Pelletized activated carbon is a highly porous substance that attracts and holds organic chemicals inside it. The media is created by first burning a carbonaceous substance without oxygen which makes a carbon “char”. Next, the “char” is treated chemically or physically to develop an interconnected series of “holes” or pores inside the carbon. The great surface area of this internal pore network results in an extremely large surface area that can attract and hold organic chemicals.
One gram of activated carbon can have a surface area in excess of 500 m2 (5,400 sq ft), with 3,000 m2 (32,000 sq ft) being readily achievable and thus provides much more surface area and higher absorption properties then a carbon mesh filter. Pelletized carbon can also be packed closer together then the carbon fibers of a mesh filter, thus leaving less space for pollutants to pass through without being absorbed.
Each Zephyr filter uses 1 pound (453 grams) of pelletized activated carbon; which as a result create an enormous surface area for absorbing odors and a long list of VOC’s commonly found in indoor air; some of which include: Formaldehyde, Benzene, Ammonia, Carbon Monoxide, Chlorine, household cleaners, off gassing from household building materials, perfumes, and many more.
STAGE 2: HEPA FILTER

HEPA Filters are one of the most trusted filtration technologies in the world, used by hospitals, high tech clean rooms, and scientific laboratories. HEPA is an acronym for “High Efficiency Particulate Air” and/or “High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance”. It is important to understand that not all HEPA Filters are made the same and thus provide differing results. Cheaper made HEPA Filters or “HEPA – type, HEPA – style or HEPA – like Filters” are made from nonwoven glass fibers (fiberglass) and thus have a lower filtration efficiency.
Our HEPA Filters are made from woven randomly arranged PP Fibers (Polypropylene Fibers) for higher filtration efficiency and PP Fibers are chemically inert, meaning they are not chemically reactive; and therefore do not pose any offsetting health risks. Our HEPA filters are designed to target much smaller pollutants and particles down to 0.1 μm in diameter and larger. These particles are trapped (they stick to a fiber) through a combination of the following three mechanisms:
Diffusion: An enhancing mechanism that is a result of the collision with gas molecules by the smallest particles, especially those below 0.1 μm in diameter, which are thereby impeded and delayed in their path through the filter; this behavior is similar to Brownian motion and raises the probability that a particle will be stopped by either interception or impaction; this mechanism becomes dominant at lower air flow.
Interception: Particles following a line of flow in the air stream come within one radius of a fiber and adhere to it.
Impaction: Larger particles are unable to avoid fibers by following the curving contours of the air stream and are forced to embed in one of them directly; this effect increases with diminishing fiber separation and higher air flow velocity.
Through these mechanisms, our HEPA Filters are effective at trapping a wide range of particulates including: Dust, pet dander, allergens, pollen, dust mites and their droppings, tobacco smoke.
STAGE 3 - ACTIVATED CARBON FILTER
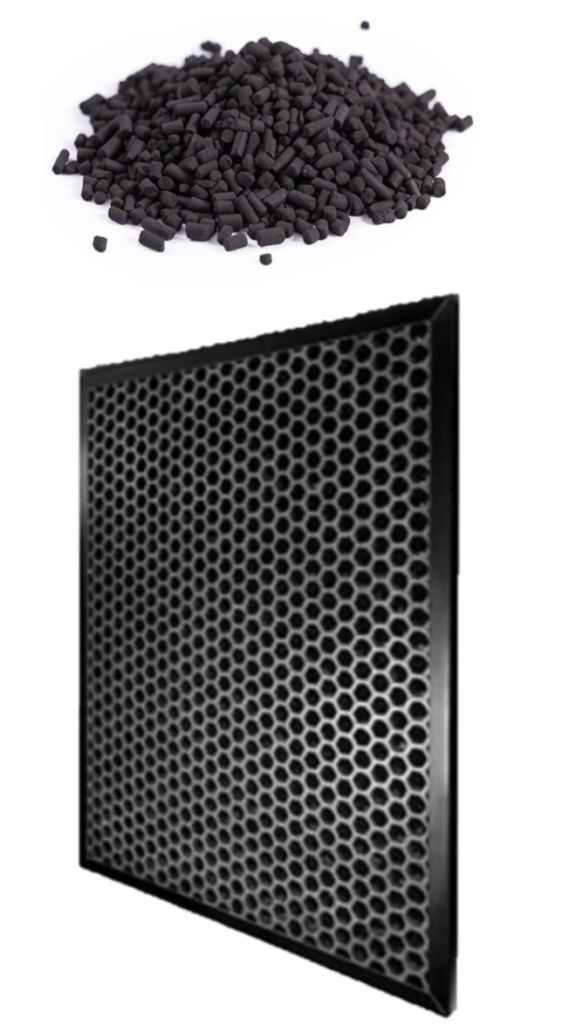
It is important to understand that not all carbon filter used in air purifiers are the same. There are two types of filters which are used in air purifiers, one is cheaper and one is more expensive; it is therefore important to understand and know which of these two types of activated carbon filters you are getting when you buy an air purifier.
The first type of filter is a carbon mesh type filter which is widely used by companies due to its very inexpensive manufacturing cost. Unfortunately, the absorption rate of this type of filter is much lower due to a much smaller surface area because there are fewer interconnected series of pores inside the carbon mesh fibers and the air space between fibers allows more pollutants to pass through then the second type of carbon filter.
The second type of carbon filter that can be used in an air purifier is pelletized carbon. Pelletized activated carbon is a highly porous substance that attracts and holds organic chemicals inside it. The media is created by first burning a carbonaceous substance without oxygen which makes a carbon “char”. Next, the “char” is treated chemically or physically to develop an interconnected series of “holes” or pores inside the carbon. The great surface area of this internal pore network results in an extremely large surface area that can attract and hold organic chemicals.
One gram of activated carbon can have a surface area in excess of 500 m2 (5,400 sq ft), with 3,000 m2 (32,000 sq ft) being readily achievable and thus provides much more surface area and higher absorption properties then a carbon mesh filter. Pelletized carbon can also be packed closer together then the carbon fibers of a mesh filter, thus leaving less space for pollutants to pass through without being absorbed.
Each Zephyr filter uses 1 pound (453 grams) of pelletized activated carbon; which as a result create an enormous surface area for absorbing odors and a long list of VOC’s commonly found in indoor air; some of which include: Formaldehyde, Benzene, Ammonia, Carbon Monoxide, Chlorine, household cleaners, off gassing from household building materials, perfumes, and many more.
STAGE 4: VITAMIN C ENRICHMENT
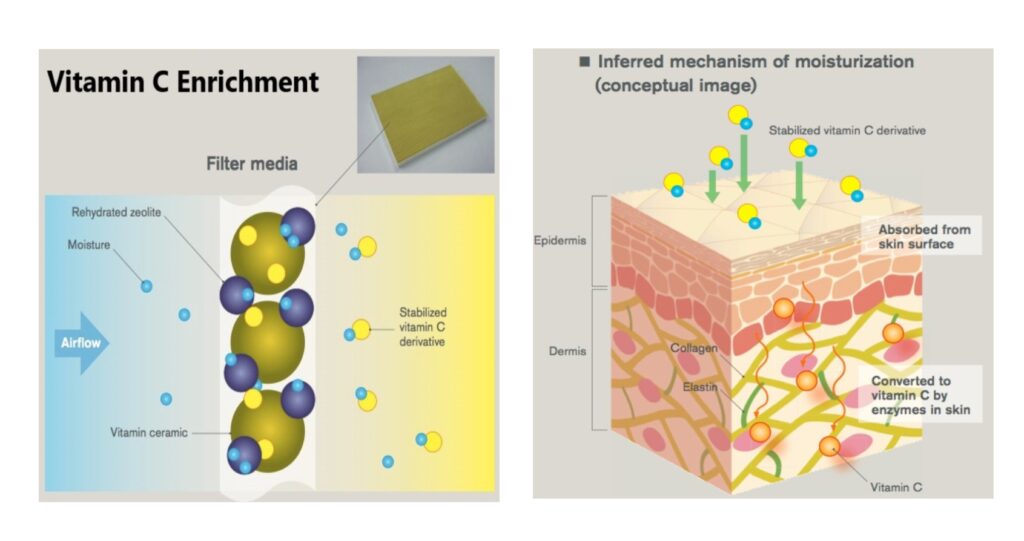
Vitamin C is essential for synthesis of collagen and elastin, which are necessary for healthy skin. It explains why all moisturizing skin creams and lotions contain Vitamin C. By mixing Vitamin C in the air purifiers air flow it ensures that your skin gets a moisturizing effect by being available directly to the skin. This technology is not new, as vehicle manufacturers have used this technology for over 20 years in their AC filters.
Zephyr adds a ceramic additive to the multi filter cartridge that releases Vitamin C when it comes into contact with the moisture naturally present in the air. Zeolite, a moisture absorbent is also added for facilitating a continuous release of Vitamin C in dry conditions.
The main intents of adding Vitamin C to the air is to assist in the natural moisturization of skin, while also possibly increasing the immune systems resistance to various viral and bacterial infections.
STAGE 5: PHOTOCATALYST FILTER (PCO)
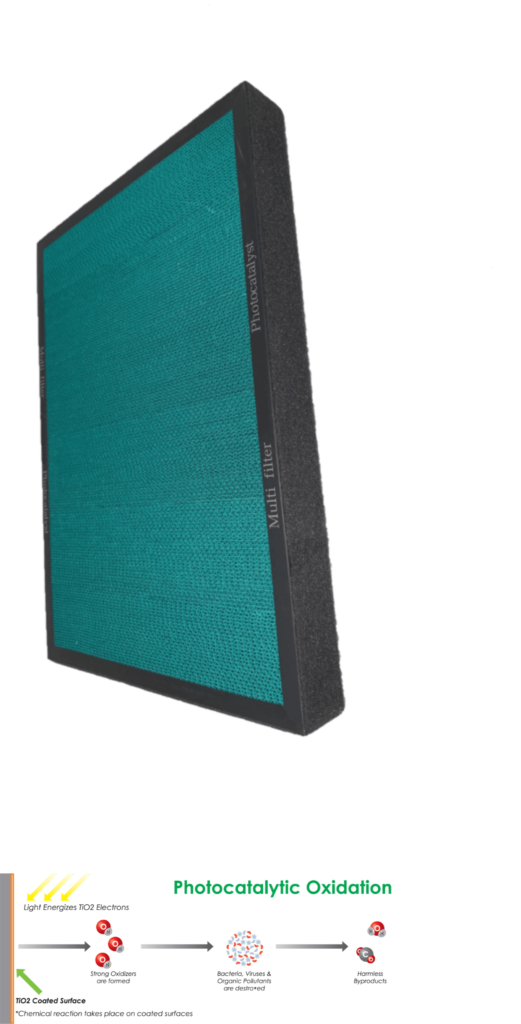
PCO technology is an extremely powerful purification method, PCO units have the ability to eliminate particles as small as 0.001 microns, including the tiny penetrating particles that can be absorbed into your lungs and cause damage. It is important to understand that PCO filters do not capture particles, chemicals or gases but instead destroy them by converting them into safer compounds through a chemical reaction called Photocatalytic Oxidation.
For years, PCO technology has been FDA approved for reducing bacteria in meat processing plants, and it’s even used to cleanse pesticides from the fruits and vegetables we eat. Essentially, PCO filtration can be summed up like this: Photocatalytic Oxidation is achieved when intense UV light is reflected onto a Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) coated filter. This process creates hydroxyl radicals and super-oxide ions, which are highly reactive electrons.
These highly reactive electrons aggressively combine with other elements in the air, such as germs, bacteria, viruses, VOC’s and toxic gases; which include harmful pollutants such as formaldehyde, Benzene, ammonia and many other common contaminates released by building materials and household cleaners generally found in the home.
Once bound together, the chemical reaction takes place between the super-charged ion and the pollutant, effectively “oxidizing” (or burning) the pollutant. This breaks the pollutant down into harmless carbon dioxide and water molecules, making the air more purified. Therefore, this type of purification technology converts harmful particulates, germs, bacteria, viruses and toxic gases into safer compounds such as carbon dioxide and water.
Photocatalytic technology goes a step beyond air filters you might have used in the past due to its ability to attack mold, viruses, and bacteria in the air and on surfaces. This capability is all but unique to an air purifier which uses PCO UV technology and cannot be expected from competitors.
Photocatalytic Oxidation Studies
1. Chemistry scientists from the University of Colorado and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado conducted an experiment testing the effectiveness of photocatalytic oxidation against harmful VOCs (volatile organic compounds such as formaldehyde and other known carcinogens). They found that destruction of these contaminates was nearly 100%.
2. Scientists working on behalf of the U.S. Department of Energy found that photocatalytic oxidation air purification may be beneficial for the large-scale treatment of air in occupied buildings, while conserving energy costs. This is due to the fact that this technology destroyed VOC chemicals at a significant rate, even at high air flow rates. Their study indicated that photocatalytic oxidation could provide as much VOC removal by itself as compared to the expensive process of introducing outdoor air into the indoor environment, drastically reducing the need to channel outdoor air inside.
3. In another study commissioned by the U.S. Department of Energy, scientists found that photocatalytic oxidation converted more than 95% of harmful VOC chemicals to harmless carbon dioxide and water molecules.
STAGE 6: UV-C GERMICIDAL STERILIZATION LAMPS
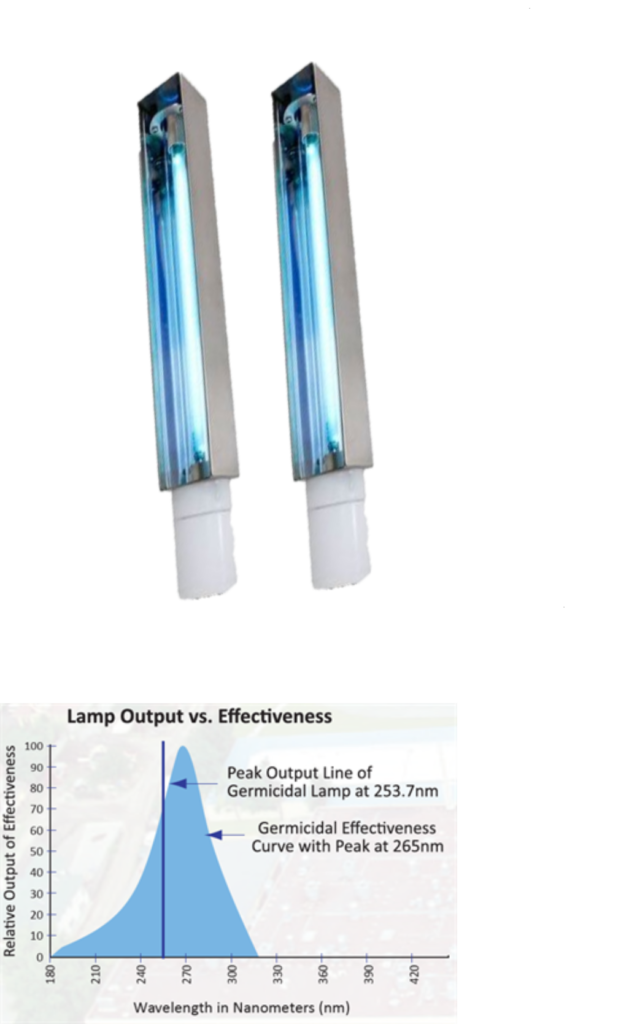

UV-C is a type of ultraviolet light, also known as Germicidal UV. UV-C light is produced naturally by the sun; however, the earths atmosphere blocks nearly 100% of it. UV-C light is different then the common UV-A or UV-B rays we are exposed to from the sun as UV-C light has a much shorter wavelength of 100nm – 280nm (nanometers). Due to the nature of the shorter wavelength, UV-C light has the power to kill or incapacitate bacteria, mold, fungi, and viruses by destroying the DNA of dangerous pathogens. This is an extremely powerful technology to facilitate clean air, because there are no known microorganisms immune to UV-C energy.
How does it work? Miniscule airborne droplets hold microorganisms that can transmit a wide range of illness and diseases such as measles, influenza, colds and tuberculosis to humans. Germicidal UV-C light has a specific wavelength of between 222nm—254nm (nanometers) that breaks the DNA of these microorganisms and prohibits them from reproducing. This range of UV light is absorbed by the DNA and RNA of microorganisms, which causes changes in the DNA and RNA structure, rendering the microorganisms incapable of replicating / reproducing. A microorganism that can’t reproduce is considered dead; since it is unable to multiply to infectious numbers within a host and are consequently harmless. Due to this, Germicidal UV-C light has been used to protect against dangerous pathogens for over 50 years. It can be used to create a safer, healthier home or office environment, and can directly help reduce the transmission of common illnesses and infectious diseases.
The Zephyr comes equipped with 2 low-pressure, mercury-arc Germicidal Sterilization Lamps which are designed to produce the highest amounts of UV-C radiation – where 90% of energy is typically generated at 254nm. This radiation is very close to the peak of the germicidal effectiveness curve of 265nm, the most lethal wavelength to microorganisms. This is important to understand, as 254nm is the peak output of any low-pressure Germicidal Lamp and the closest wavelength to the most lethal 265nm wavelength that can be achieved.
STAGE 7: NEGATIVE IONS

The final step in the Zephyr’s 7 Stage Filtration process is our Ion Generator which releases millions of negatively charged ions into the indoor air.
Negative ions are odorless, tasteless, and invisible molecules that we inhale in abundance in certain outdoor environments. Think mountains, waterfalls, and beaches. Negative ions are produced naturally outdoors by plants, trees, lightning, rain, waterfalls and ocean waves crashing onto the shoreline which is also known as the Lenard effect. When inhaled and they reach our bloodstream, negative ions are believed to produce biochemical reactions that increase levels of the mood chemical serotonin, helping to alleviate depression, relieve stress, and boost our daytime energy.
The science behind Negative Ions: Ions are molecules that have gained or lost an electrical charge. They are created in nature as air molecules break apart due to sunlight, radiation, and moving air and water. You may have experienced the power of negative ions when you last set foot on the beach or walked beneath a waterfall. While part of the euphoria is simply being around these wondrous settings and away from the normal pressures of home and work, the air circulating in the mountains and the beach is said to contain tens of thousands of negative ions — Much more than the average home or office building, which contain dozens or hundreds, and many register a flat zero.
The Zephyr uses a negative ion generator also known as a Chizhevsky’s chandelier, which is a device that uses high voltage to ionise (electrically charge) air molecules. Negative ions, or anions, are particles with one or more extra electrons, conferring a net negative charge to the particle. Cations are positive ions missing one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. By electrically charging air molecules just prior to them exiting the Zephyr, an extra electron is added to these molecules resulting in molecules with a net negative charge.
What this does, is introduce a naturally occurring and beneficial event which happens everyday outdoors by way of plants, trees, rain, waterfalls and the ocean; and brings those benefits to your indoor air at home or the office.
There are three main achievements that result from increasing the presence of negative ions to indoor air. First, negative ions attach to positively charged dust particles and pollutants in the air and help draw them out of suspension where their ability to remain airborne is greatly diminished. Second, negative ions help to freshen indoor air; creating an outdoor / nature type environment. Last but not least, when inhaled and they reach our bloodstream, negative ions are believed to produce biochemical reactions that increase levels of the naturally produced mood chemical serotonin, helping to alleviate depression, relieve stress, and boost our daytime energy.
